
AQL stands for Acceptable Quality Limit, and it is a statistical measurement used to determine whether the quality of a batch or lot of products meets the buyer's requirements. It helps to assess whether a production lot should be accepted or rejected based on a sample from the lot.
The AQL standard helps manufacturers and suppliers assess the level of defects in a production lot and decide whether the lot meets the customer’s acceptable quality criteria. It provides a consistent and uniform method to determine the level of defects that is tolerable for the buyer and what would be considered unacceptable, leading to rejection.
AQL is typically calculated based on a sample from a batch, with specific defect types classified as critical, major, or minor. Different AQL values are set for each category:
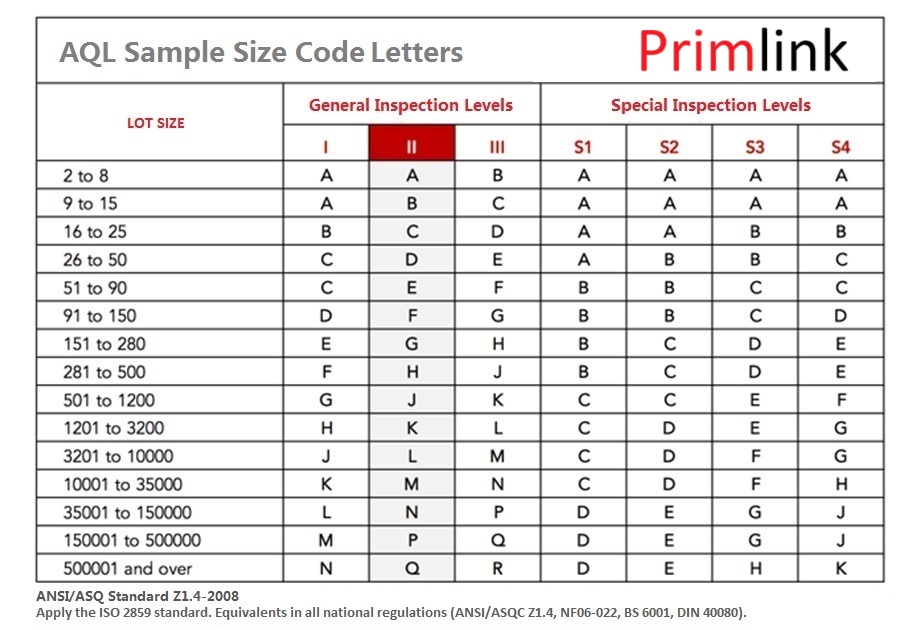
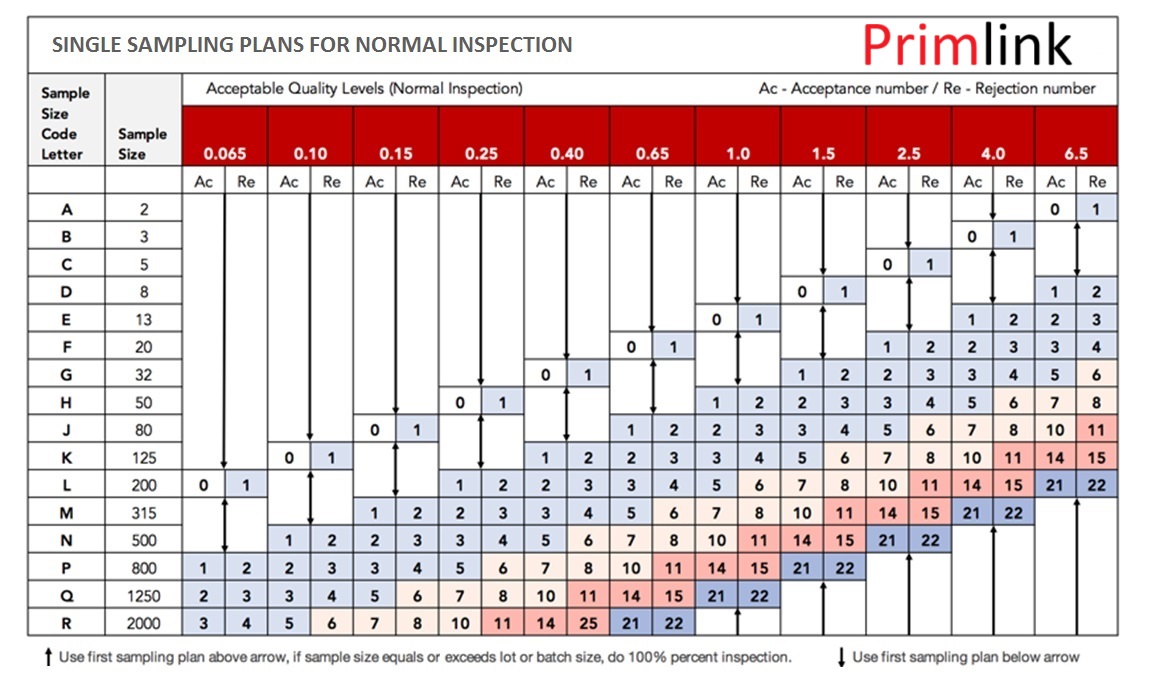
The AQL value indicates the maximum number of defects allowed in a sample size. If the number of defects exceeds the set limits, the lot is rejected. The process involves:
The AQL values can be selected based on the level of quality required by the buyer. The most common AQL values are:
The inspection level determines the sample size to be selected for inspection, with three standard levels:
Once the inspection is complete, the results are compared to the acceptance and rejection criteria for the sample size and AQL level:
For a batch of 5000 units with an AQL of 2.5%, the sample size may be 200 units, and the acceptance number could be 10 defects. If more than 10 defects are found in the sample, the batch would be rejected.